What is the Difference Between Ionic Bond and Covalent Bond?
when two or more atoms are linked together, they form a molecule or compound. there are two types of chemical bonds i.e., ionic bond and covalent bond. the basic Difference Between Ionic Bond and Covalent Bond is that an Ionic bond is a chemical link between two atoms due to the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions in an ionic compound while a covalent bond is a chemical link between two atoms or ions where electron pairs are shared between them.
In this post, you are going to learn about the Ionic Bond vs Covalent Bond step by step with Diagrams.
- An overview
- Comparison table
- What is an Ionic Bond?
- What Is a Covalent Bond?
- Lots more
So if you want to get benefits from this post you’ll love this post.
Let’s Dive right in..
An Overview
the atoms are always made the bond between one another and create compounds and molecules. hence, a bond is a chemical process that is occurred due to the attraction of two or cluster of atoms between each other. it is produced due to the presence of an electrostatic force of attraction. these chemical bonds can be classified on the basis of strength they have in them.
some bonds are known as strong bonds while others are said to be weaker bonds. furthermore, the stronger bonds are sub-divided into two types i.e., ionic bond and covalent bond.
so, we are here to know the difference between these two strong bonds.
Difference Between Ionic Bond and Covalent Bond in Tabular Form | |
Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond |
Definition | |
| The bond between metal and nonmetal is known as an ionic bond. The nonmetal attracts the electron, so it’s like the metal donates its electron to it. | The bond between two nonmetals with similar electronegativity is known as a covalent bond. Atoms share electrons in their outer orbitals. |
Polarity | |
High | Low |
Boiling Point | |
High | Low |
State at Room Temperature | |
Solid | Liquid or Gas |
Shape | |
No definite shape | Definite shape |
Melting Point | |
High | Low |
Chemical Species | |
| Metal and nonmetal (remember hydrogen can act either way) | Two nonmetals |
Examples | |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl), Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4 ) | Methane (CH4), Hydrochloric acid (HCl) |
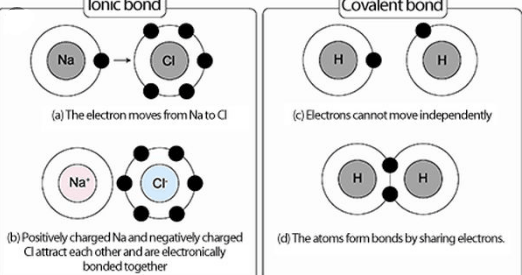
What is an Ionic Bond?
an ionic bond is a chemical bond that formed between two atoms one from metal and the other from non-metal. in this bond, an electron is shared or delivered from one side to another i.e., one atom release an electron, and another gain an extra electron. the metal ion which loses electron gain a negative charge on it while the other that loses has a positive charge on it.
due to the positive and negative charge, these ions attract each other strongly with electrostatic force and make a crystal lattice. usually, ionic compounds are found in the form of solids that have high melting points and are highly soluble in water.
besides this, they have high electrical conductance. to make such types of bonds electronegativity difference must be greater than 1.7 or equal to that.
the common characteristics of the compounds with ionic bonds are as follows:
- It is formed by the complete transfer of an electron from one atom to another.
- high melting and boiling points.
- Two bonded atoms always dissimilar.
- It is usually formed between the metal and non-metal of groups I and II and the non-metals of groups VI and VII of the periodic table.
- they have the ability to remain in a solid-state when at room temperature.
- Ionic compounds are soluble in the water.
- It is non-directional that is not represented by any line or arrow.
- possess a crystalline or transparent structure.
- They can conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
What Is a Covalent Bond?
A covalent bond is another strong bond that is occurred between two adjacent atoms(non-metallic ones) to form a stable octet by sharing their outermost electrons. a stable balance between the attractive and repulsive forces of the atoms of covalent bonds is present. as a result of sharing electrons with each other, they makeup shells and achieve a stable electronic configuration.
covalent bonds are sub-divided into three types of bonds i.e., single, double, and triple covalent bonds depending on the ability that how many electrons they share. every shared electron makes a strong bond. when the electronegativity difference between the atoms is not enough to produce an ionic bond, as a resultant, a covalent bond is formed.
the electronegativity difference between the atoms less than 1.7 is necessary for the formation of such bonds.
the common characteristics of the compounds with covalent bonds are as follows:
- It is formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms.
- act as insulators from electrical current and heat.
- Two bonded atoms either similar or dissimilar.
- It is usually formed between non-metals.
- soft in the solid-state as compare to ionic bonds.
- Covalent bonds are insoluble in water.
- It is a directional bond and represented by the complete line.
- they have low melting and boiling points.
- Polar molecules of covalent bonds are only soluble in polar solvents.
- Nonpolar molecules of covalent bonds are soluble in nonpolar solvents.
You May Also Like:
Good answer but not in the level of class 10