What are Branches of Science?
According to different scientists, there are three main branches of science: Earth science, physical science, and life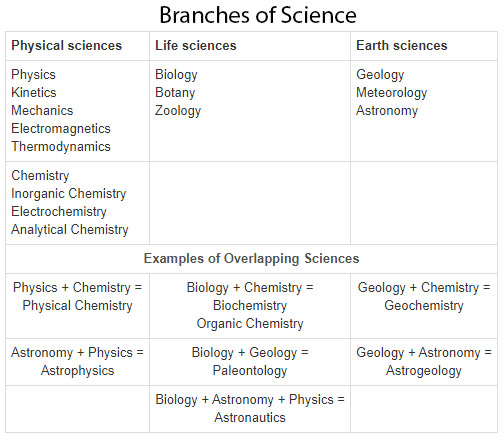 science. earth sciences typically deal with the study of solid earth e.g air and water. it also classified into many other sub-branches like atmospheric science, geological and hydraulic sciences, etc.
science. earth sciences typically deal with the study of solid earth e.g air and water. it also classified into many other sub-branches like atmospheric science, geological and hydraulic sciences, etc.
physical sciences are related to natural sciences and deals with the study of nonliving things while life science is the study of living things and most accurately life.
to dig deeper into branches of science, let’s quickly look at the definition of science.
What is Science?
the word “Science” is derived from the Latin meaning “to Know”. Science is a way of knowing or study of nature. science emerges from our curiosity about ourselves, the world, and the universe. In general, it means describing realities and providing answers to the various questions of human thinking by systematically ordered knowledge of anybody.
The significance of Studying Science
- helps us to understand the natural world.
- science is concerned with information gained by observing and testing the natural world.
Basis of Science
to understand natural world science ask the following questions.
- how did a variety of living things evolve on earth?
- in what way do they interact?
- what processes must occur in each organism?
- why living things differ from nonliving ones?
What are the 7 sub-branches of Science?
the major science branches are further subdivided into many other sub-branches and disciplines. bellow we have some examples and sub-branches with definitions.
- Chemistry
- Computer science
- Biology
- Physics
- Mathematics
- Economics
- Types of Science
What is Chemistry?
chemistry is that branch of science that is dedicated to the study of the structure, properties, composition, and transformation of matter after undergoing various processes or reactions that affect its molecules and atoms. it is an experimental science that studies matter, its properties, and its changes in nature. And is that all matter is made up of simple chemical elements or their compounds, each with its own differential characteristics.
It is worth mentioning that matter is everything that surrounds us, composed of molecules and atoms that react to various chemical changes, and that it can be related to the release of energy in some cases.
Chemistry studies are conducted in laboratories and use the scientific method. This has allowed the discovery of various subjects, their compositions, how they are related or transformed. Hence, elements that are basic in other scientific studies have been discovered.
Examples of Sub-Branches of Chemistry
- Acid-Base Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Environmental Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Nuclear Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Solid State Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Astrochemistry
- Biological Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Geochemistry
- Materials Science Photochemistry
- Radiochemistry
- Stereochemistry
- Surface Chemistry
Chemistry is the study of the composition of substances and how they interact with each other.
It covers topics such as:
▸ How the chemical and physical properties of substances are determined by their structure at an atomic scale.
▸ How substances can change the form, such as between solid, liquid, and gas, as well as through processes such as dissolving.
▸ How substances can interact and their particles rearrange to form new substances.
▸ Energy changes involved in physical and chemical processes.
▸ The classification of matter into groups such as elements, compounds, and mixtures.
Physics
Examples of Sub-Branches of Physics
- Molecular Physics
- Classical Physics
- Modern Physics
- Applied Physics
- Experimental Physics
- Theoretical Physics
- Computational Physics
- Atomic Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Mechanics Nuclear Physics
- Particle Physics
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Field Theory
- Quantum Mechanics
- Special Relativity
- General Relativity Theory
- Thermodynamics
Physics is the study of natural phenomena from the smallest sub-atomic particles to entire galaxies.
It covers topics such as:
▸ The motion and interaction of moving objects.
▸ Forces such as magnetism, gravity, and electrostatic forces.
▸ Waves, including light, sound, and electromagnetic radiation.
▸ Energy and heat, and how they can be transferred and transformed.
▸ Electricity and electrical circuits
Biology
Examples of Sub-Branches of Biology
- Botany
- Zoology
- Microbiology
- Ecology
- Genetics
- Molecular Biology
- Medicine
- Conservation Biology
- Cell Biology
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Biotechnology
- Developmental Biology
- Marine Biology
- Parasitology
- Taxonomy
- Nursing
- Dentistry
- Evolutionary Biology
- Toxicology
- Mycology
- Phycology
- Radiobiology
- Virology
Biology is the study of living things.
It covers topics such as:
▸ How a range of living things have evolved on Earth over millions of years.
▸ The diversity of living things, including animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms.
▸ How the features of living things are related to the functions that their body systems perform.
▸ How living things are interdependent and interact with each other and their environment.
▸ The life cycles, adaptations, and behaviors of living things, and how these features aid survival.
▸ The structure of cells, and the vital life processes they perform.
▸ How characteristics are inherited from one generation to the next.
Earth Science
Examples of Sub-Branches of Earth Science
- Environmental Science
- Climatology
- Geophysics
- Physical Geography
- Geology
- Oceanography
- Geomorphology
- Meteorology
- Glaciology
- Geodesy
- Hydrology
- Volcanology
- Seismology
- Limnology
- Palynology
- Edaphology
- Paleoclimatology
- Paleoecology
Earth science is the study of Earth, including its oceans and atmosphere, as a system.
It covers topics such as:
▸ The formation of the earth.
▸ The structure of the earth, including the different types of rocks.
▸ The processes involved in shaping the earth, such as plate tectonics, weathering, and erosion.
▸ The resources of the earth and the influence of human activity.
Space Science
Examples of Sub-Branches of Space Science
- Astronomy
- Cosmology
- Astrophysics
- Planetary Science
- Stellar Astronomy
- Galactic Astronomy
- Planetary Geology
- Radio Astronomy
- Microwave Astronomy
- Infrared Astronomy
Space science is the study of our solar system, stars, galaxies, and the universe.
It covers topics such as:
▸ The Big Bang and the formation of the universe.
▸ The formation of our solar system.
▸ How the relative positions and movement of Earth, the moon, and the sun interact to create day and night, seasons, and other events such as eclipses.
▸ How the moon affects the earth, such as in the formation of tides.
▸ Other planets and moons within our solar system and beyond.
▸ The sun and the life cycle of stars.
- Exact Sciences
- Applied Sciences
- Factual Sciences
- Human Sciences
- Pseudo Sciences
- Empirical Sciences