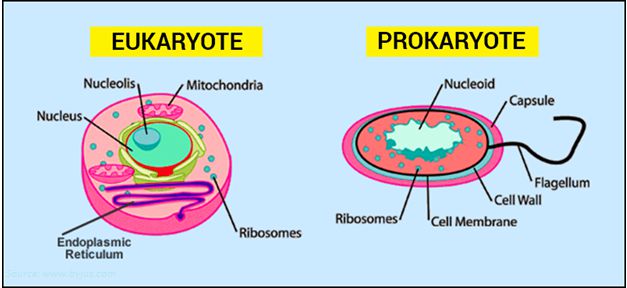
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
All the cells basically are evolved from the same single common cell. this cellular world belongs to a specific branch of biology called cell biology. cell biology states that there are two major types of cells: prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The Major Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells is that Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound nucleus and organelles, cell size ranges from 0.5um to 100um While Eukaryotic Cells have a membrane-bounded nucleus, cell size ranges from 10um to 150um.
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells in Tabular Form
| Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
| 1.Prokaryotic cells do not have well-defined nuclei. They do not have a nuclear membrane. The nuclear material (DNA) is directly submerged in the cytoplasm. | 1.Eukaryotic cells do not have well-defined nuclei. They have a nuclear membrane. |
| 2. The organism possessing prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. | 2. The organism possessing eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. |
| 3. Prokaryotes lack membranous bound organelles. For example, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic reticulum, and Chloroplast are absent in prokaryotes. | 3.They contain all membranous bound organelles. |
| 4.Prokaryotes have a small ribosome of the 70S. | 4.They have large ribosomes of the 80S. |
| 5. In prokaryotes, mitosis is absent and the cell divides by binary fission. Prokaryotes are primitive organisms. | 5. Their cells are divided by mitosis. The eukaryotes are advanced organisms. |
| 6. The cell wall of the prokaryotes is made up of peptidoglycan or murein. In this case, the polysaccharide chain is bound with the short chain of amino acids. | 6. Only plants have cell walls. The cell wall of plants is composed of cellulose. |
| 7. Examples: Bacteria and Blue-Green Algae (cyanobacteria) | 7. Examples: all other animals and plants, fungi, and Protista. |
See Also: Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Replication
Summary – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
we know that both types of cells have certain organelles and cell structures in them. The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells highly dependent on the size and absence and presence of these structures and organelles.
- the eukaryotes are typically larger than prokaryotes. they are more than 10 microns long and complex.
- prokaryotes are usually 10 microns long and have a simple structure as compared to eukaryotes.
- the nucleus, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles are only present in eukaryotic cells.
- prokaryotic cells are known as independent unicellular organisms.
- the eukaryotic cells are live unicellular in some cases but mostly constitute complex multicellular organisms
- in prokaryotic cells asexual reproduction is present while the eukaryotes are consist of both types of reproduction i.e., asexual and sexual.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition and Characteristics
the word originated from the Greek “eu” having means “true” and “the Karyon” with meanings “nucleus”. so, we can say that Eukaryotic cells are those having nucleus within their cellular structure.
this nucleus defines the nucleus and also organizes it in a proper way. the Eukaryotes also have a very complex system or organelles in which the mitochondria are present for producing energy for cells. this energy is utilized by the cell to feed and grow better.
on the other hand, the chloroplast stands out in photosynthetic organisms while the cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus are also present in these cells. they manufacture multiple chemical components of cell membrane such as cell movement.
being unicellular, they can move freely or from a group and can organize their way of life. An example of free-living of such type organisms is amoeba from the Protista kingdom or yeast from the fungi kingdom. on the other hand, being able to form groups or colonies, all the animals of kingdom Animalia and kingdom Plantae are considered as examples of such organisms.
Prokaryotic cell Definition and Characteristics
Prokaryotes are also derived from the Greek word “Pro” having means “before” giving the concept that they are the first existing type of cells from others. in contrast to eukaryotes, The prokaryotes are known as the most diversified cells, old and simplest organisms.
they are always flooded with cellular life in different habitats on the planet. the common examples of such types of cells are the animals of kingdom Monera ( bacteria and archaea etc.)
they have shown an un-well organized matrix internal structure while analyzing on an electron microscope. also, the cell wall surrounds it as a resistance protective layer.
they have a variable morphology such as spiral, spherical, or rod-like shapes. they can divide rapidly through asexual reproduction with the presence of the ability to exchange generic or genetic materials. these abilities are carried out mostly through the cell walls and cell membranes.
Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Previously, we have seen some differences between the two types of cells but there are also some eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- both types of cells are considered the basic and fundamental unit of life for different organisms.
- they are unicellular as well as multicellular organisms that can adapt, evolve and colonize and habitat of the earth.
- both, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have a structure consisting of membranes that are filled with generic information or DNA. they also have enzymatic machinery which consequences different vital functions for the body like growth, feeding, development, and reproduction of organisms, etc.
- the energy is necessary for the survival of life, hence, both types of cells interchange or converts the energy on a consistent basis from one form to another to survive and evolve.
- with this changing of energy mechanism, they also keep a relationship with the exterior environment to give the response of different chemical and biological sources.