3 stages of the Calvin cycle| Summary, Products, Equations
(Light Independent or dark reactions)
[wp_ad_camp_1]
“The cyclic series of reactions, catalyzed by respective enzymes by which carbon is fixed and reduced, resulting in the synthesis of sugar during the dark reactions of the photosynthesis is called Calvin cycle.”
The dark reaction takes place in the stroma of chloroplast. These reactions do not require light energy directly. They can occur in the presence or absence of light. They need only assimilatory power (stored compounds) in the form of ATP and NADPH. These compounds are produced during light reactions. So energy is stored in these compounds.
This stored energy of these compounds is used for the synthesis of carbohydrates form the CO2. These reactions can be summarized as follows:
The detail of the path of the carbon in these reactions was discovered by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues at the University of California. Calvin was awarded Nobel Prize in 1961.
[wp_ad_camp_2]
The Calvin cycle can be divided into three phases: Carbon fixation, Reduction and regeneration of CO2 acceptor.
Phase 1 in Calvin cycle: Carbon fixation
In this step, initial incorporation of three molecules CO2 takes place into the organic material. The molecule of CO2 reacts with a highly reactive phosphorylated five carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RUBP). This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme called ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. This enzyme is commonly called Rubisco.
The rubisco is the most abundant protein in the chloroplast. It is perhaps the most abundant protein on the earth. The product of this reaction is a highly unstable six carbon compound. This compound immediately breaks into two molecules of three carbon compounds, called 3-phosphoglycerate (phosphoglyceric acid PGA).
The 3-phosphoglycerte is a three carbon compound. The carbon of the CO2 has been fixed now. Earlier this carbon was part of the CO2. Now it is a part of an organic molecule (phosphoglycerate).
The product of initial carbon compound is a three carbon compound. Therefore, The Calvin cycle is also known as “C3 pathway”.
[wp_ad_camp_3]
Phase 2: Reduction
- Each molecule of the PGA receives an additional phosphate molecule from the ATP (coming from light energy) and forms 1, 3 biphosphoglycerate.
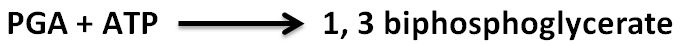
- The NADPH (coming from light reaction) donate its electrons to 1, 3 biphosphoglycerate. So it is reduced to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). This G3P sugar is also formed by the splitting the glucose molecule during glycolysis. In this way fixed carbon is reduced to energy rich G3P. The G3P (not glucose) is the carbohydrate produced during Calvin cycle.
During Calvin cycle, three molecules of CO2 and three molecules of RUBP (five carbon compounds) are used. They produce six molecules of G3P (containing 18 carbon in all). Only one molecule of G3P out of six molecules leaves the cycle and is used for making glucose, sucrose, starch or other carbohydrates.
The other five molecules are recycled to regenerate the three molecules of five carbons RuBP. The RuBP is a CO2 acceptor. So, only one molecule of G3P can be counted as net gain of carbohydrates.
Phase 3: Regeneration of CO2 acceptor, RuBP
[wp_ad_camp_4]
The carbon skeletons of the five remaining molecules of G3P (three carbon compound) are rearranged through a complex series of reactions.
They form a five carbon compound ribulose phosphate (RuP). The RuP is phosphorylated and becomes ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). The RuBP is the five-carbon CO2 acceptor. It is the same compound with which the cycle was started. More molecules of the ATP (coming from light reaction) are used for the phosphorylation of three RuP molecules. These RuBP are now prepared to receive more CO2 again. In this way this cycle continues.