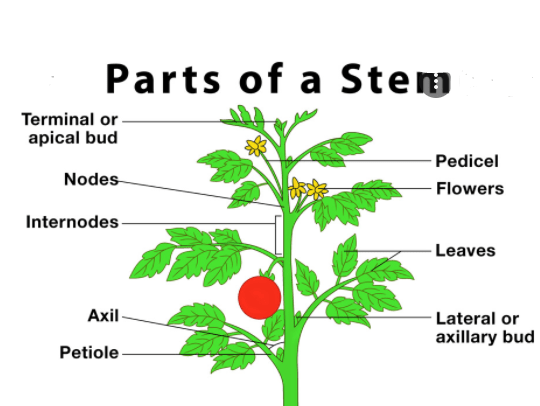
Parts of a Stem
The aerial part of the plant is called the stem. the major function of the stem is to provide support and to make the structure of a plant or tree. however, Neck, Knots, Internodes, Armpit, Vegetative apex, and buds are the major parts of a stem.
What is the stem?
the part of a plant that grows in the opposite direction of the root is simply known as a stem which brings nutrients, water, and other minerals & salt to all the parts of a plant. it also facilitates the exchange of energy from the sunlight. this energy produces during the process of photosynthesis. however, a stem have several other characteristics such as:
- the yémula or plumule of a seed embryo are basic sources of origination of the stem.
- it provides support to the pant fruits, flowers, and leaves.
- there are terminal buds located on the stem which help to sprout new flowers and branches.
- it has negative geotropism which causes them to go in the opposite direction of gravity or earth.
- it also has positive phototropism which gives them a direction to go in the forward direction of light.
Parts of the Stem and their Functions
the structure of a stem can be divided into many parts such as:
- Neck: this part is located right at the junction between the root and the beginning of it.
- Knots: they are small nodules that appear along the stem and that indicate the birth of the leaves.
- Internodes: are the spaces between two consecutive nodes. In general, the internodes diminish as we approach the apex of the stem.
- Armpit: it is the exact point of union between the branch and the leaf.
- Vegetative apex: located at the end of the stem, it is a set of meristematic cells in a constant process of separation and protected by a cluster of leaves that gives rise to what is known as the terminal bud. From here, the flower and the fruit will be born.
- Buds: they are the small buds that appear in each armpit and that indicate the growth of a new branch. The buds are held by an insertion point between the leaf and the axilla and there are several types: the terminal buds, located at the upper end, the lateral buds, generally located between the nodes, and the adventitious buds, which are located at the Whole plant.
Types of Stems
In general, we can classify the stems by their consistency, duration, and medium in which they live.
Stem types According to Their Consistency
- Woody: typical of trees and shrubs.
- Semi-woody: typical of flowering plants or riverside plants.
- Herbaceous: typical of vegetables and wild plants.
Stem Types According to Their Duration
- Annuals: typical of plants with one year of life.
- Biannuals: typical of plants with two years of life.
- Perennials: typical of trees and large shrubs.
Stem Types According to the Environment
- Aerial stems.
- Underground stems.
- Aquatic stems.
What are Aerial stems?
The aerial stem has four major types:
- Stem: one that offers consistency to herbaceous
- Trunk: a woody stem that generally takes a cylindrical shape and is found in trees and shrubs.
- Cane: semi-woody stem, also cylindrical in shape, formed by knots and internodes that, on occasion, are usually hollow and have sheathing leaves.
- Stipe: a cylindrical stem that usually ends in a tuft of leaves and with a single terminal. Name by which the stem of palm trees is known.
Underground stems
They are classified into rhizomes, tubers, and bulbs. Sometimes they are confused with roots.
- Rhizomes: horizontally growing stems have buds on their upper face and in turn, make aerial organs to facilitate the storage of reserve substances.
- Tubers: stems thickened with stored reserve substances that also have buds capable of creating a new plant.
- Bulbs: stems composed of a single structure that widens to produce several buds in the upper part, and with adventitious roots in the lower part. Generally spherical in shape and covered by a bed of scaly leaves to protect the seed.
Aquatic stems
They are what make up aquatic plants, whether they are fixed, floating, or submerged. They are normally of a very intense green color and a fleshy texture.
We invite you to discover this topic in more detail with this other Green Ecology article on the different types of stems.
What are the Functions of Plant Stem
After knowing the parts of the stem and the specific functions of each one, we can approach the issue of the functions that the stem has in the structure of a plant.
- Support the entire aerial.
- Transport nutrients and substances through the interior part.
- Transport the raw sap from the root until it reaches the leaves thanks to the use of the stem ducts, where it is enriched with carbon dioxide and the so-called processed sap is created, the main food of the plant.
You May Also Like: