Phylum Nematoda Characteristics, Examples, and Classes
Nematodes (Aschelminthes-The Round Worms)
The name Nematoda means pointed ends. These animals have elongated 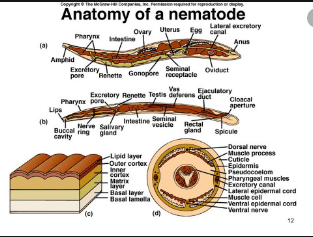 worm like body with pointed ends. One end of the body is called anterior end. However, the head is not clearly demarked. There are no special sense organs at this end.
worm like body with pointed ends. One end of the body is called anterior end. However, the head is not clearly demarked. There are no special sense organs at this end.
General Characters of Phylum Nematoda
- The nematodes are triploblastic.
- They show bilateral symmetry. Their body is unsegmented.
- They are pseudocoelomate. The body cavity is called pseudocoel. It is derived from the hollow space, the blastocoel. Blastocoel is formed in blastula stage during embryological development. So their coelom is not formed form mesoderm. Pseudocoel has a large number of vacuolated cells (cells with vacuoles). These cells are filled with a protein — rich fluid. This fluid produces high hydrostatic pressure (pressure due to fluid).
- They have different sizes. Nematoda may be microscopic or some nematodes having up to one meter length.
- They have tube like digestive system. It is in the form an alimentary canal with two openings. Mouth is present at anterior end and anus is present at the posterior end. A fluid filled space is present between the body wall and the alimentary canal. So it forms tube within tube” type structure in nematods. The digestive system of parasitic forms is simple.
- The excretory system consists of excretory canal. These canals run longitudinally and unite at the anterior end to form a single canal. This canal open outside through an excretory pore on the ventral surface.
- There is a nerve ring around the pharynx. It gives rise to dorsal, ventral and lateral nerve cords. These nerves run throughout the length of the body of worm. Their sense organs are in the form of sensory papilla. It is present on the lips at the anterior end.
- These systems are absent in nematods. The exchange of gases takes place through general body surface
- Locomotion takes place by muscles. These muscles contract and relax and produce undulating waves. These muscles are arranged in four bands. Two are dorso-lateral and two are ventro-lateral. The circular muscles are absent. So, they can bend only dorso-ventrally.
- Reproduction: The sexes are separate. The female gonads are ovaries and these produce eggs. The male gonads are testes and these produce sperms. A larval stage is present during their life cycle.
Importance of Phylum Nematoda
Parasitic diseases
Aschelminthes has many important parasites. These bacteria cause some very serious diseases in man and plants.
- Ascaris Lumbericoides: It is an intestinal parasite of man.
- Rhabditis: This genus contains many species. They are found in soil, organic matter, water and feces of man and animals.
- Enerobius Vermicularis: It is commonly known as pinworm. It is present everywhere but it is more common in Europe and America.
Pinworm is a parasite of human caecum, colon and appendix (parts of large intestine). Their movement cause intense itching of anus. It also causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the colon and appendix. It results in insomnia and loss of appetite.
- Acyclomstoma duodenale: It is commonly known as hookworm. It is a parasite of human small intestine. Hookworm is found in Asia, North Africa and Europe.
It is a very dangerous parasite. Hookworm holds the villi of intestine and suck blood and body fluid. It produces an anticoagulant during feeding. This anticoagulant prevents the clotting of blood. It leaves the wound bleeding after feeding. It cause severe anemia in children and retard (stop) the physical and mental growth.
Round Worms as Decomposer
Round worms are present every outdoors. They play an important role in the breaking of down of organic matter. A single rotting apple may contain 90,000 worms. Billions of worms are present in each acre of topsoil (upper part of soil).
Other Related Phylums:
- Phylum Porifera Charachteristics & Examples
- Phylum Chordata Characteristics & Classification
- Characteristics of Phylum Echinodermata
- Phylum Mollusca Characteristics and Examples
- Phylum Arthropoda Characteristics and Examples
- Phylum Annelida Characteristics and Examples
- Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics and Examples
- Phylum Coelenterata/Cnidaria Characteristics and Examples
- Phylum Porifera/Sponges With Examples & Characteristics
- Phylum Protozoa: Characteristics & Groups/Classes