Difference between Left and Right Kidney
the Major Difference between Left and Right Kidney is that the left kidney is approximately at the vertebral level T12 to L3 and sits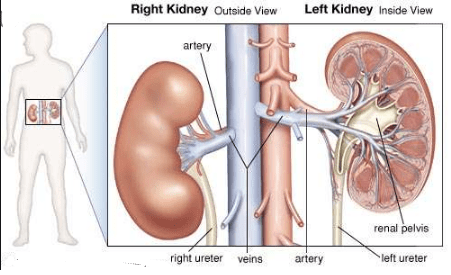 below the diaphragm and posterior to the spleen while the Right Kidney is slightly lower to the vertebral level T12 to L3.
below the diaphragm and posterior to the spleen while the Right Kidney is slightly lower to the vertebral level T12 to L3.
the left kidney is positioned slightly higher on the left side of the body related to ribs 11 and 12 and the right kidney is positioned slightly lower and the right side of the body near rib 12. the left kidney is slightly larger in size than the right kidney. the left kidney blood is severed by the left renal artery while in the right kidney, blood is severed by the right renal artery.
What is a kidney?
Each kidney is about 11 to 14 feet long, about 6 cm wide, and about 3 cm wide. Each kidney has millions of features called nephrons. The kidney is surrounded by a nerve called the gallbladder. The bark, cord, pelvis, and hilum are important organs of the kidney. In addition, a large part of the renal artery enters the kidney.
The main function of the kidneys is to cleanse chemicals and blood vessels that enter the arteries. These products are eliminated from the bloodstream like urine. In addition to excretion, homeostasis, osmoregulation, regulation of salt in the body, regulation of pH and hormone production are also important functions of the kidney.
Functions of kidneys
The main function of the kidneys is to maintain the digestive system. This means that they control the amount of water, salt, and other metabolic processes in the body.
They perform many actions:
Waste disposal
The kidneys eliminate a number of wastes and eliminate them in the urine. The two main elements that the kidneys eliminate are:
- urea, caused by protein breakdown
- uric acid from the nucleic acid breakdown
Nutrient absorption
The kidneys absorb nutrients into the blood and transport them to where they best support health. They also resist other products to help maintain the digestive system.
Desaturated products include:
- glucose
- amino acids
- bicarbonate
- sodium
- water
- phosphate
- chloride, sodium, magnesium, and potassium ions
Maintain the pH
In humans, the acceptable acidity level is between 7.38 and 7.42. Below these limits, the body enters hypoxia and, above all, alkaline ischemia.
Outside of this range, proteins and enzymes break down and can no longer function. In special cases, this can be fatal. The kidneys and lungs help maintain a constant level of acidity in the human body. The lungs do this by bringing together the concentration of carbon dioxide.
The kidneys control acidity with two processes:
- Reabsorbs and renews urinary bicarbonate: bicarbonate helps neutralize acids. The kidneys can hold it back if the acidity is tolerable or release it if the level of acidity increases.
- Excretion of hydrogen ions and solid acids: solid or unstable acids are all acids that do not appear due to carbon dioxide. They are due to the imperfect metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. They contain lactic acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid.
Regulation on osmolality
Osmolality is a measure of the body’s saline water balance or the relationship between fluids and minerals in the body. Dehydration is the main reason for the electrolyte balance. If osmolality increases in plasma, the hypothalamus in the brain responds by sending a message to the pituitary gland. This, in turn, releases diabetes mellitus (DHA).
In response to DHA, the kidney makes several changes, including:
- increased urine levels
- greater water absorption
- opening of the part of the collection duct in which water normally cannot enter, allowing water to return to the body
- keep urea in the kidney marrow rather than expel it because it sucks water
Blood pressure regulation
The kidneys monitor blood pressure if necessary, but are responsible for a slower adjustment. They regulate long-term blood pressure causing changes in the fluid outside the cells.
They work with other measures to increase renal absorption of sodium chloride or salt. This effectively increases the extracellular compartment and increases blood pressure.
Secretion of active compounds
Erythropoietin: controls erythropoietin or red blood cell production. The liver also produces erythropoietin, and whose kidney is the main producer in adults.
Pure: helps control the widening of the arteries and the volume of plasma, lymph, and interstitial fluid. Toxic is a liquid that contains white blood cells that support immunity and the interstitial fluid is the main component of the extracellular fluid.
Calcitriol: it is the active hormonal metabolite of vitamin D. It increases both the amount of calcium that the intestines can absorb and the absorption of phosphate in the kidneys.
What is the left kidney?
The left kidney is located on the left side of the body and has 11 heels and 12 ribs, usually, the left kidney is 0.5 to 1.5 cm longer than the right kidney. When considering connections between neighbors, the frontal kidney of the left kidney is associated with the left hemisphere, arteries, stomach, colonic changes in the intestine, as well as fasting where the surface connects the rib11 to rib12, at the diaphragm, psoas head, quadratus lumborum, muscles of the body’s transverse muscles and transverse process of the L1 vertebra.
What is the right kidney?
The right kidney is located on the right side of the body, relative to the ribs12. The frontal lobe of the right atrium is associated with the right caudal part, the liver, the descending rear part of the duodenum, positive intestinal changes, and the small intestine.
In addition, the right kidney is composed of ribs12, diaphragm, psoas head, quadratus lumborum, spinal cord, and L1 vertebrae.
Structure
In humans, the kidneys are located in the abdomen, one on the side of the spine, and have a slight position in circulation. The asymmetry of the pelvis, caused by the condition of the liver, leads to the cross. the right kidney is smaller than the left kidney and grows to the left. middle as the left kidney.
The left kidney is estimated at levels T12 to L3 and the right side is lower. The kidneys are below the diaphragm and are located in the liver. The left kidney is placed under the diaphragm and enters the uterus. In addition to all the kidneys, there are adrenal injuries. That is the reason for the difference between the Left and Right Kidneys. Each kidney, with its adrenal gland, is composed of two fatty acids: the fatty acids between the kidney and the fatty acids and the fat. fat is better than kidney stones.
The bean-like face kidney has a double face. The lower part of the border is the pelvis relative to the kidney, while the kidney is located around the kidney and ureter. Surrounded by kidney stones, kidneys, surrounding fat, kidney fat, and internal fat.
The anterior (temporal) head of the body is the peritoneum, while the anterior (posterior) head is the transverse fascia. The upper part of the kidney arm is involved in the liver. The left kidney is part of the cavity. Both, so go inside when you breathe.
Inside, the kidneys are deep and distinctive. The renal parenchyma can be divided into two main areas: the posterior cortex and the medulla. The cortex enters the spinal cord, which is divided into three parts: these are called renal pyramids.
The pyramid is called the papilla. Each papilla with a name and a name is associated with a characteristic chalice, which collects urine from the pyramid. Many small calcastar joints join together to form a large calyx. Urine passes through the most common arteries of the pelvis in relation to the kidney and the process dissolves and develops. From the pelvis to the kidney, urine enters the ureter, which transports it to the bladder for greater safety.
The center of each kidney has a deep pole, called the hilum nerve. It functions as a kidney transplant door – normal vessels in the kidney and ureter enter/remove the kidney through this process.
The key differences between the Left and Right Kidney
The key difference between the Left and Right Kidneys is their position and size. The left kidney is generally smaller and more stable than the right kidney.
The kidney is the same organ that is located on both sides of the vertebral body, as well as the cavity in the neck just below the diaphragm. However, there is a slight difference between the Left and Right Kidneys.
Difference between Left and Right Kidney
The difference between the Left and Right Kidneys is their height and size. The size of the left kidney is larger than the size of the right kidney. In addition, the left kidney is positioned higher than the right kidney due to the asymmetry in the internal cavity caused by the liver.
Another difference between the Left and Right Kidneys is that the left kidney serves the blood to the left kidney while the right kidney works for the right kidney. In addition, the front and rear sides of the left and right kidneys are linked to neighboring buildings.
Summary
In short, the kidneys are two layers on both sides of the spine; to be precise, they are located on the abdominal wall under the diaphragm. The main difference between the Left and Right Kidneys is their position and size because the left kidney is slightly larger and more visible than the right kidney.
You May Also Like: