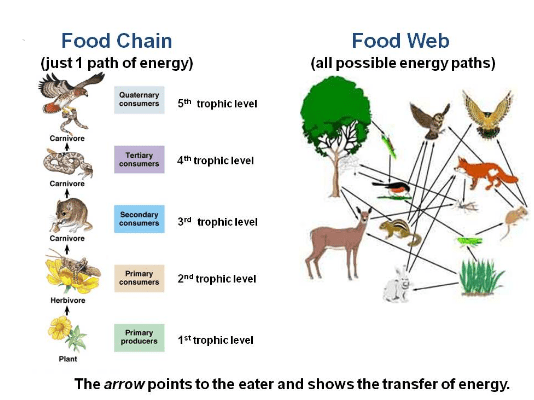
what is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
the basic difference between the food chain and the food web is that The food chain is a diagram that describes the process of the transfer of nutritional or food substances through the species that make up an ecosystem and shows how each living thing gets its food, also describes how energy and nutrients are passed through one to another creature while A Food web is a graphic representation of the interconnection that occurs between the different food chains, this graphic indicates that animal consumes different animals through a consumer-resource scheme.
there are different energy producers, consumers, and also decomposers. they all are interconnected with food chains and these chains create a food web. the food chain starts with plant life and ends up with animal life and the food web is the converse.
difference between a food chain and a food web in Tabular Form
| Food chain | food web |
| Definition | |
| Describe the process by which nutrients are transferred between the different animals that make up an ecosystem. | It is the representation of the connection between the food chains that make up an ecosystem. |
| Representation | |
| It represents the transfer of energy from one animal to another through food. | Represents predators and prey connecting them by the link that unites them as producing organisms (plants), consumers (carnivores and herbivores), and decomposers (fungi and bacteria) |
| Consequences | |
| It has no effect on the improvement in the adaptability of organisms, that is, it does not define the possible improvements that a living being can have to adapt to its environment. | Food webs are more complex and can represent an improvement in the competitiveness and adaptability of an organism. This means that a creature can adapt to compete against other animals that consume the same food or that consume it as food. This is why mimicry arises, muscles adapted to the race, larger claws, etc. |
| Representation | |
| It represents a single pathway and lines through which energy and nutrients travel in an ecosystem. That is to say: Producers-consumers of the first order-consumers of the second order-decomposers. | It represents the number of interconnected food chains through which energy and nutrients travel in an ecosystem. It also represents the stability of an ecosystem. The greater the presence of complex interactions between autotrophs, mixotrophs, and heterotrophs, the stability increases. On the other hand, if there are isolated food chains, the ecosystem is very unstable. For example, creatures that only consume a particular species of plant or predators adapted to consume one or two species of animals. |
| a series of organisms that feed one another. | consists of no. of food chains involving many organisms web. |
| they are less adaptive. | they are more adaptive in comparison to the food chain. |
| the one individual in the food chain contains or occupies one tropic level. | one individual in the food web can contain or occupy several tropic levels. |
What is a Food chain?
It is a graphic method that allows describing the natural process by means by which nutrients are transmitted
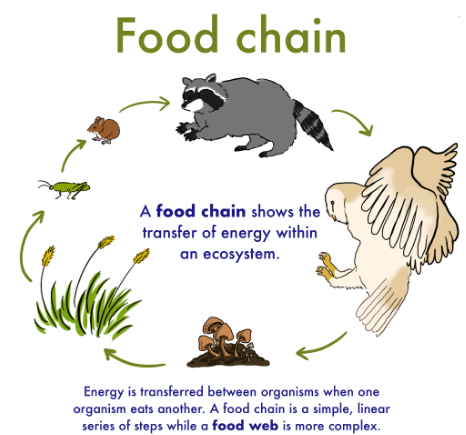
between the different animal species that make up an ecosystem. In the food chain, a species consumes as food the one that follows it, and this, in turn, consumes the species that precedes it.
For example, a cow consumes grass and receives energy from it, in turn, the cow is consumed by wolves, who receive energy and nutrients from their meat; the wolf is eaten by fungi, bacteria, insects, and scavengers, thus completing the food chain.
The food chain represents the transfer of energy and nutrients between different species. Each link obtains the energy necessary for its vital processes from the previous link. In each link, there is a loss of energy in each transfer or consumption.
This means that plants receive the purest energy because they convert inorganic matter into organic matter through photosynthesis. This energy is used by herbivores and in turn, the meat and bones of herbivores are used by carnivores, who receive less energy. according to the law of conservation of energy, energy neither created nor destroyed but only flows from one level to the other with the help of different organisms.
In the food chain, living beings are organized into four groups:
- Producers: They are the plants or beings that feed through photosynthesis.
- First-order consumers: They are herbivorous animals.
- Second-order consumers: They are carnivorous animals.
- Decomposers: They are all those that consume the remains of other living beings, decompose them and allow them to become part of the soil as inorganic matter.
Types of Food chains:
there are two types of food chains such as:
- detritus food chain
- Grazing Food chain
What is the detritus food chain?
The detritus food chain contains various types of species consisting of plants and organisms, for example, algae, fungi, bacteria, protozoa, worms, and insects. The detritus food chain always starts from dead organic materials.
what is the Grazing Food chain?
The grazing Food chain starts with green plants which pass it to herbivores and carnivores. while this process, tropic levels acquire their energy from photosynthesis.
What is a food web?
It is a graphic representation of the connection between different food chains. It usually represents the species that
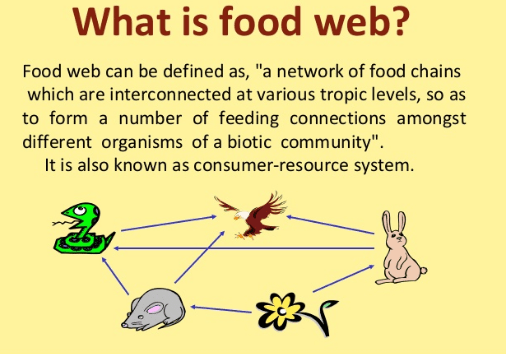
consume each other, indicating the link between the producing, consuming, and decomposing organisms.
Trophic networks are also known as the consumer-resource system, this allows ecologists to classify living beings in trophic levels:
Autotrophs: they are those creatures that produce their own food, they are the base of all food chains and trophic web. They can be plants, algae, and photosynthetic creatures. These creatures produce organized matter from inorganic substances. The energy necessary to carry out this transformation is obtained from the sun or hot springs.
Heterotrophs: these are those animals that need to consume other creatures to take advantage of their nutrients in order to grow, develop, and reproduce. They can be herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores.
Mixotrophs: they are autotrophic creatures that can also obtain organic matter by consuming other creatures. An example is carnivorous plants.
The food web illustrates the consumption routes of living beings, that is, it represents how heterotrophic species feed on autotrophs and in turn, on other heterotrophs. It is a simple way of representing all the relationships that exist in an ecosystem and on which its balance depends.
In a food web, we can find small photosynthetic organisms such as plankton up to large trees, small parasites, and insects up to large predators such as the tiger or the lion. Viruses and bacteria are also represented in these chains, as they form their own food chains.
Examples
- Primary Consumers: small Insects, rabbits, lizards, mice, rodents, and earthworms.
- Secondary Consumers: Tarantulas, owls, foxes, scorpions, robins, lizards, hawks, and snakes.
- Tertiary Consumers: foxes, Hawks.
- Producers: acacias, Cacti, flowers, bushes, brush.
Applications:
- interaction of different species can be described clearly.
- describes the energy transfer of different levels in an ecosystem.
- used to study community structure from top to bottom and vice versa.
- the illustrations of interactions between all kinds of species are made with the food web.
You May Also Like: