7 functions of the cell membrane with Structure & Composition
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) or Plasmalemma is the outer most layer of the animal cell while in plant cell; it is present inside of the cell wall. It consists of proteins and phospholipids.
in other words, the nucleous and cytoplasm in all types of cells is enclosed in a membrane called cell membrane.
7 Functions of Plasma OR Cell Membrane
Plasma OR Cell Membrane performs following functions:
[wp_ad_camp_1]
- Transport of Material
Transport of material is an important function of the plasma membrane. It forms a barrier between the cell contents and outer environment.
- Differentially permeable membrane
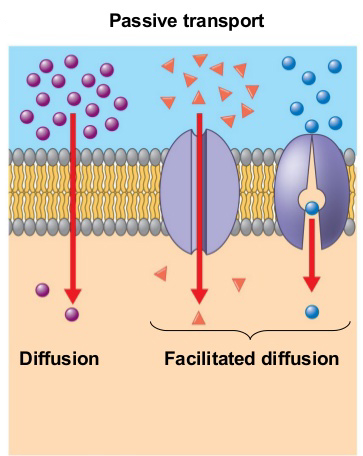
The plasma membrane allows only selective substance to pass through it. So, it is called differentially permeable or selectively permeable membrane.
- Maintenance of concentration gradient
The plasma membrane regulates the flow of materials and ions. So it maintains a definite concentration gradient. Lipid soluble substances easily cross the membrane. Similarly, many small gas molecules, water, glucose etc. are neutral compounds.
[wp_ad_camp_2]
So they easily cross the membrane. While, ions like Na+, K+ is charged particles. So, they cannot cross the membrane easily. Thus, there is unequal distribution of substances between inside and outside the cell.
The unequal distribution of substances causes passive transport or diffusion. “The movement of molecules from the area of higher concentration to the area of low concentration is called diffusion or passive transport.”
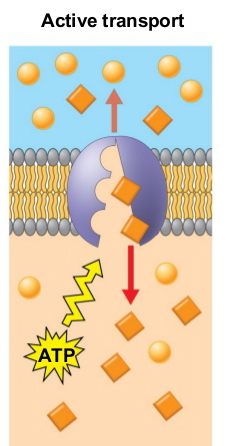
The movement of molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration by the expenditure of energy is cell active transport. This transport takes place against the concentration gradient. The energy used for this movement is provided by ATP.
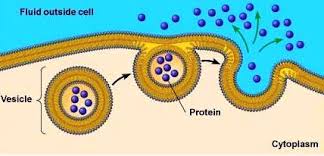
The intake of food material by in-folding of the membrane in the form of vacuole is called Endocytosis. It takes place in many animal cells. There are two types of Endocytosis:
- Phagocytosis: or cell eating. In this case, solid particles are engulfed by in-folding of membrane.
- Pinocytosis: or cell drinking. In this case, liquid material is taken inside by in-folding.
[wp_ad_camp_3]
- Transmission of Nerve Impulses
The cell membranes of the neurons (nerve cells) transmit the nerve impulses from one part of the body to the other part. It keeps coordination in the body.
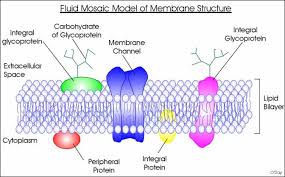
Structure of Plasma Membrane or Cell Membrane
The structure of cell membrane was proposed by two scientists, Singer and Nicholson. Their structure is called Fluid Mosatic Bilayered mode of cell membrane. Different biologists proposed different structures of the plasma membranes. These are as follows:
According to this model, the cell membrane is composed of lipid bilayers. These lipid bilayers are sandwich between inner and outer layer of protein. This basic structure is called unit membrane. This unit membrane is present in all the cellular organelles like mitochondria, Golgi bodies. The modern technology could not prove this model.
According to this model, the proteins do not form a continuous layer. It is not present only on the outer surface. Proteins are embedded in the lipid bilayers in a mosaic manner. Fluid mosaic model was proposed on the basis of this discovery. This is most acceptable model. The cell membrane contains charged pores. Movement of material takes place through these charge pores by diffusion or by active transport.
[wp_ad_camp_4]
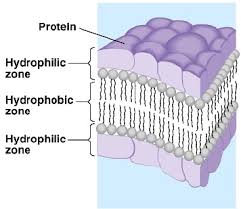
The cell membrane has Bilayered structure i.e. it consists of two layers of Phospholipids, upper layer and lower layer. The phospholipids form the major parts. Each layer consists of two parts.
- Hydrophilic End
It is the outer end of two layers also called Polar End and considered as water-soluble. These are situated at the upper and lower parts of cell membrane.
- Hydrophobic End
These are non-polar and water insoluble. These are present towards inner side and are present opposite to each other.
Chemical Composition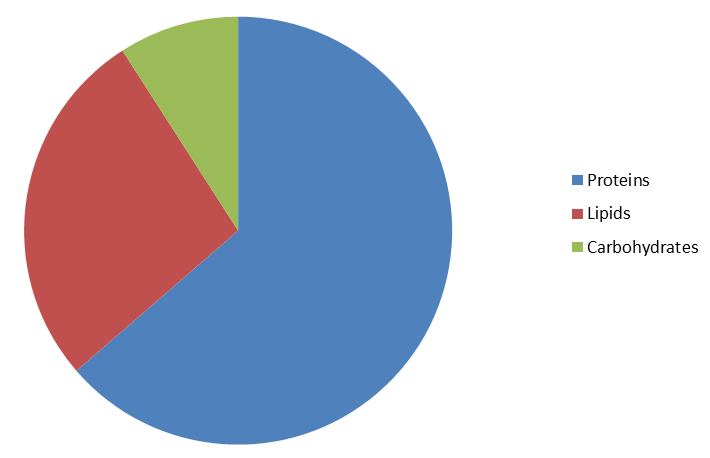
Cell membrane is chemically composed of lipids and proteins:
Proteins are 60% to 80%
Lipids are 20% to 40%
A small amount of carbohydrate is also present.
The lipids molecules are found in a fluid condition, rotating and moving within the membrane. These lipids also contain proteins which are of two types;
- Extrinsic Proteins (peripheral proteins)
There proteins are present along the surface of the lipids. They have loose attachment with membrane surface.
- Intrinsic Proteins (integral proteins)
These proteins are found deeply in the lipid layer. They help in the movement of water-soluble ions outside or inside the cell.
The proteins are associated with lipids, called lipoproteins or associated with carbohydrates are celled glycoproteins. The proteins are found like a mosaic within the cell membrane, so the model is celled fluid mosaic model.